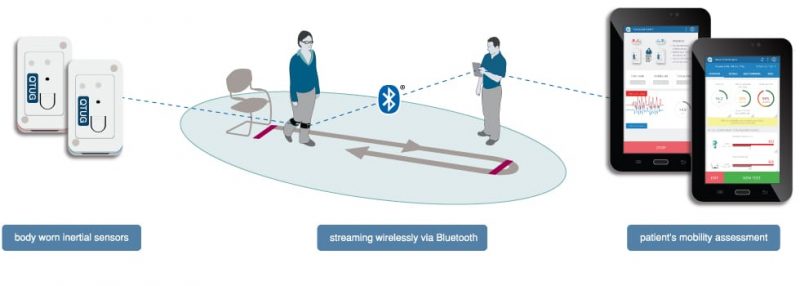
Our research is your technology!
Our products, QTUG (Quantitative Timed Up and Go) and Kinesis Gait, falls risk and gait assessment technologies have been developed through nine years of research and extensively clinically validated through publication in top-tier international scientific journals.
Supporting Clinical and Scientific Evidence
- Key evidence and findings
- NICE briefing on QTUG technology
- Case Studies on Kinesis technologies
- Supporting evidence – Peer reviewed journal papers
- Supporting evidence – Peer reviewed conference papers
- QTUG cost saving and fall prevention economic model
Kinesis products have been shown to be Valid, Reliable and Accurate in measuring Gait and Mobility, while as well as assessing Falls in older adults.
The technology is based on nine years of peer reviewed research. Our technology uses advanced wearable sensors suitable for objective assessment of gait and mobility, measurement of response to rehabilitation and treatment and well as screening for falls risk, mobility impairment and frailty.
Kinesis Health Technologies Ltd are a spin-out from University College Dublin and the TRIL centre, a large ageing research project funded by Intel, GE Healthcare and the Irish government.
Key findings of research to date
- QTUG has been shown to be more accurate than standard measures (manually timed TUG test and Berg balance scale) in assessing risk of falling in older adults.
- QTUG has been shown to provide a robust and reliable estimate of patients’ frailty state.
- Inertial sensor algorithms contained in Kinesis Gait and QTUG have been validated against gold standards for assessment of temporal and spatial gait parameters (optical motion capture system, forceplate and GAITRite).
- QTUG has been validated both prospectively and cross-sectionally, and shown to provide an accurate measure of falls risk in older adults.
- Mobility parameters derived using Kinesis Gait and QTUG have been shown to provide valid and reliable measurement of gait and mobility in: patients with multiple sclerosis, older adults and healthy controls.
- Change in mobility parameters obtained using QTUG have been shown to be associated with cognitive decline in older adults.
NICE briefing
NICE, The UK National Institute of Health and Care Excellence have recently issued a briefing note on the QTUG technology and its utility in assessing falls risk and frailty. Click here to read the briefing note.
Case studies
- QTUG used to assess a nursing home based fall prevention exercise programme – Herfordshire Care Providers Association (HCPA), Hertfordshire, UK.
- Use of QTUG in a hospital outpatient setting – St Vincents hospital, Dublin, Ireland.
- Use of QTUG in a community fall prevention service – Irishtown Primary Care Centre, Dublin, Ireland.
- Use of QTUG for risk stratification in a sheltered housing organisation – Circle housing, Kent, UK.
Internationally peer reviewed journal papers
The effect of a dual task on Quantitative Timed Up and Go (QTUG) performance in community-dwelling older adults a preliminary study
Erin Smith, Lorcan Walsh, Julie Doyle, Barry Greene, Catherine Blake
Geriatrics & Gerontology International 2016. In press. DOI: 10.1111/ggi.12845
Fall risk assessment through automatic combination of clinical fall risk factors and body-worn sensor data
Barry R. Greene, Stephen J. Redmond, Brian Caulfield
IEEE J. Biomed Health Inform 2016. 21(3). DOI: 10.1109/JBHI.2016.2539098
Assessment and classification of early stage multiple sclerosis with inertial sensors: comparison against clinical measures of disease state
Barry R. Greene, Stephanie Rutledge, Iain McGurgan, Christopher McGuigan, Karen O’Connell, Brian Caulfield, Niall Tubridy
IEEE J. Biomed Health Inform 2015. Jul;19(4):1356-61.
The reliability of the quantitative timed up and go test (QTUG) measured over five consecutive days under single and dual-task conditions in community dwelling older adults
Erin Smith,Lorcan Walsh, Julie Doyle, Barry Greene, Catherine Blake
Gait & Posture 2016, (43): 239-244
Classification of frailty and falls history using a combination of sensor-based mobility assessments
Barry R. Greene, Emer P Doheny, Rose A. Kenny and Brian Caulfield
Physiological Measurement, 2014, 35 (10), 2053
Frailty status can be accurately assessed using inertial sensors and the TUG test
Barry R. Greene, Emer P Doheny, Aisling O’Halloran, Rose A. Kenny
Age and Ageing, 2014, 43(3): 406-411
Evaluation of falls risk in community-dwelling older adults using body-worn sensors
B. R. Greene, E. P. Doheny, C. W. Walsh, C. Cunningham, L. Crosby, and R. A. Kenny
Gerontol. 58(5), 2012
Quantitative falls risk assessment using the timed up and go test
Barry R. Greene, Alan O’Donovan, Roman Romero-Ortuno, Lisa Cogan, Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, Rose A. Kenny
IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010. 57(12): p. 2918-26
Assessment of cognitive decline through quantitative analysis of the timed up and go test
B. R. Greene, R. A. Kenny
IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(4) p988-995, 2012
Stability of daily home-based measures of postural control over an 8-week period in highly functioning older adults
Denise McGrath, B. R. Greene, K.J. Sheehan, L. Walsh, R. A. Kenny, B. Caulfield
Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015 Feb;115(2):437-49
Falls classification using tri-axial accelerometers during the five-times-sit-to-stand test
Emer P. Doheny, Barry R. Greene, Cathal Walsh, Timothy Foran, Clodagh Cunningham, Chie Wei Fan and Rose Anne Kenny
Gait and Posture, 2013, I38(4): 1021-1025
A comparison of algorithms for body-worn sensor based spatio-temporal gait parameters to GAITRite electronic walkway
Greene BR, Foran T, McGrath D, E.P. Doheny, Burns A. Caulfield, B.
Journal of Applied Biomechanics; 28(3):349-55, 2012
Early identification of declining balance in higher functioning older adults, an inertial sensor based method
KJ Sheehan, BR Greene, C Cunningham, L Crosby, RA Kenny
Gait & Posture, 2014, 39(4): 1034-1039
Effects of a low-volume, vigorous intensity step exercise programme on functional mobility in middle-aged adults
Emer P. Doheny, Denise McGrath, Massimiliano Ditroilo; Jacqueline Mair, Barry R. Greene, Brian Caulfield, Giuseppe De Vito, Madeleine Lowery
Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2013, 41(8): 1748-1757
Quantitative falls risk estimation through multi-sensor assessment of standing balance
Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Lorcan Walsh, Emer P. Doheny, David McKeown, Chiara Garattini, Clodagh Cunningham, Lisa Crosby, Brian Caulfield, Rose A. Kenny
Phys Meas. 33 (2012) 2049–2063
An adaptive gyroscope based algorithm for temporal gait analysis
B. R. Greene, D. McGrath, R. O’Neill, K. J. O’Donovan, A. Burns, and B. Caulfield
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, vol. 48, Issue 12 (2010), p. 1251
Estimation of minimum ground-clearance (MGC) using body-worn inertial sensors
Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Cathal Walsh, Brian Caulfield
J. Biomech. 44, 1083-1088 (2011)
Diurnal variations in the outcomes of instrumented gait and quiet standing balance assessments and their association with falls history
Emer P. Doheny, Barry R. Greene, Timothy Foran, Clodagh Cunningham, Chie Wei Fan and Rose Anne Kenny
Phys Meas, 33(3), p361, 2012
Gyroscope based assessment of temporal gait parameters during treadmill running
Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Brian Caulfield
Journal of Sports Biomechanics July 2012, p1-7
Technology Innovation Enabling Falls Risk Assessment in a Community Setting
Ni Scanaill, C., Garattini, C., Greene, B. R., & McGrath, M. J.
Ageing International, vol 35, No. 4. 2010
SHIMMERâ„¢ – A Wireless Sensor Platform for Non-invasive Biomedical Research
Adrian Burns, Barry R. Greene, Michael J. McGrath, Terrance J. O’Shea, Benjamin Kuris, Steven M. Ayer, Florin Stroiescu, Victor Cionca
IEEE Sensors, Volume: 10, Issue: 9 (2010), 1527-1534
Internationally peer reviewed conference papers
- Marie Mc Carthy, Bill Byrom, Brenda Reginatto, Susie Donnelly, Barry R Greene, J Patrick Bewley, Willie Muehlhausen, Oisin Kearns. “The Reaches Study: Design of an Innovative Patient Centric Trial in a Novel Setting”, International Conference on Frailty and Sarcopenia Research, 2017.
- Ruth M. Maher, Devon G. Cota, Sonal Sheth. “Determining contributing factors to outcome measure scores using triaxial wearable sensor technology in an individual using a straight cane and ankle-foot orthosis”, APTA CSM 2017 Orthopaedic Section, (Abstracts OPO1–OPO24) 2017.
- Grace Coakley, Dara Meldrum. “Quantitative Timed Up and Go to measure falls risk and frailty levels in elderly patients post hip fracture”. 64th Annual and Scientific Meeting of the Irish Gerontological Society, Kilarney Oct 2016, Age and Ageing, Volume 45 Issue suppl 2, 2016.
- Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Brian Caulfield. “A comparison of cross-sectional and prospective algorithms for falls risk assessment”. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Conference, Chicago, 2014.
- Barry R. Greene, Michael Healy, Stephanie Rutledge,Brian Caulfield, Niall Tubridy, “Quantitative assessment of multiple sclerosis using inertial sensors and the TUG test”. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Conference, Chicago, 2014
- Emer Doheny, Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Lorcan Walsh, David J. McKeown, Clodagh Cunningham, Lisa Crosby, Rose Anne Kenny, Brian Caulfield, “Displacement of centre of mass during quiet standing assessed using accelerometry in older fallers and non-fallersâ€, IEEE EMBC 2012 conference
- Denise McGrath, Emer Doheny, Lorcan Walsh, David J. McKeown, Clodagh Cunningham, Lisa Crosby, Rose Anne Kenny, Nicholas Stergiou, Brian Caulfield, Barry R. Greene, “Taking balance measurement out of the laboratory and into the home: discriminatory capability of novel centre of pressure measurement in fallers and non-fallerâ€, IEEE EMBC 2012 conference
- Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Timothy G. Foran, Emer P. Doheny, Brian Caulfield, ‘Body-worn sensor based surrogates of minimum ground clearance in elderly fallers and controls’, EMBC 2011
- Lorcan Walsh, Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Adrian Burns, Brian Caulfield, ‘Development and Validation of a Clinic Based Balance Assessment Technology’, EMBC 2011.
- Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, Barry R. Greene, Emer Doheny, Karol O’Donovan, Terrance Dishongh, Alan D. O’Donovan, Tim Foran, Clodagh Cunningham, Rose Anne Kenny, ‘Clinical Gait Assessment of Older Adults using Open Platform Tools’, EMBC 2011
- Emer P. Doheny, Chie Wei Fan, Timothy Foran, Barry R. Greene, Clodagh Cunningham and Rose Anne Kenny, ‘An instrumented five times sit to stand test used to examine differences between fallers and non-fallers’, EMBC 2011.
- Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Emer P. Doheny, and Brian Caulfield, ‘Reliability of Quantitative TUG measures of mobility for use in falls risk assessment’, EMBC 2011
- Lorcan Walsh, Barry R. Greene, Adrian Burns, Cliodhna Nà Scanaill, “The Unobtrusive Assessment of Daily Activity and Gait Velocity”, Pervasive Health 2011 AAL Workshop
- Emer P. Doheny, Barry R. Greene, Chie Wei Fan, Rose Anne Kenny, ‘Changes in the stride length and stride velocity of fallers and non-fallers during dual task walking‘, EUGMS 2010
- Chiara Garattini, Barry R. Greene, Stefan Müller, Emma Fortune, Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, ‘Investigating Usage for a Quantitative Automated Version of the Timed Up and Go test (TUG)’, EUGMS 2010
- Barry R. Greene, Alan O’Donovan, Roman Romero-Ortuno, Lisa Cogan, Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, Rose A. Kenny , “Quantitative Falls risk assessment using body-worn sensors†EUGMS
- T Foran, CU Cunningham, CW Fan, B .R. Greene, C. Ni Scanaill, R. A. Kenny, ‘Orthostatic hypotension and postural sway: a possible cause for falls in the morning’, EUGMS 2010
- Emer Doheny, Barry R. Greene, Timothy Foran, Clodagh Cunningham, Chie Wei Fan, Rose Anne Kenny, ‘Diurnal variations in the five times sit-to-stand test for fallers and non-fallers’. EUGMS 2010
- Barry R. Greene, Chie. W. Fan, Alan O’Donovan, Timothy G. Foran, Clodagh Cunningham, Rose A. Kenny, ‘Wireless sensor measurement of diurnal variation in postural sway in older adults: home-based study’. EUGMS 2010
- Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Ross O’ Neill, Karol O’Donovan, Adrian Burns, Brian Caulfield, ‘Adaptive estimation of temporal gait parameters using body-worn gyroscopes’. EMBC 2010
- Emer Doheny, Tim Foran, Barry R. Greene, ‘A single gyroscope method for spatial gait analysis’. EMBC 2010
- Adrian Burns, Emer Doheny, Barry R. Greene, Tim Foran, Dan Leahy, Karol O’Donovan, Michael J. McGrath (SHIMMERâ„¢: ‘An Extensible Platform for Physiological Signal Capture’. EMBC 2010.
- Barry R. Greene, Alan O’Donovan, Roman Romero-Ortuno, Lisa Cogan, Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, Rose A. Kenny. ‘Falls risk assessment through quantitative analysis of TUG’ presented at the 1st AMA-IEEE Medical Technology conference on Individualised Healthcare, Washington D.C., 21-23 Mar 2010
- Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Karol O’Donovan, Brian Caulfield, ‘The use of shimmer to detect stride time in running gait. ISEA conference.
- Denise McGrath, Barry R. Greene, Karol O’Donovan, Brian Caulfield, SHIMMER: A new tool for long-term, extra-laboratory gait monitoring. ESMAC, London, 2009
- Zoran Škrba, Brian O’Mullane, Barry R. Greene, Member, Cliodhna Ni Scanaill, Chie Wei Fan, Aaron Quigley, Paddy Nixon, ‘Objective real-time assessment of walking and turning in elderly adults’, Proceedings of the 31st International Conferences of the IEEE-EMBS Conference, Minneapolis, 2009.
- Karol J. O’Donovan, Barry R. Greene, Denise McGrath, Ross O’Neill, Adrian Burns, Brian Caulfield, ‘SHIMMER: A new tool for temporal Gait analysis’, Proceedings of the 31st International Conferences of the IEEE-EMBS Conference, Minneapolis, 2009.